In the UK, the landscape of digital identity verification is rapidly evolving, especially within the realms of commercial and public sectors. Anti-fraud professionals are continually adapting to the challenges posed by sophisticated cyber threats and the complexities of digital transactions…
Historically, identity verification in both sectors primarily relied on physical documents and in-person checks. However, with the digital transformation of services and the increasing prevalence of online transactions, this traditional approach has proven inadequate. The rise of identity theft, phishing, and other forms of cyber fraud necessitates a more robust and dynamic approach to identity verification.
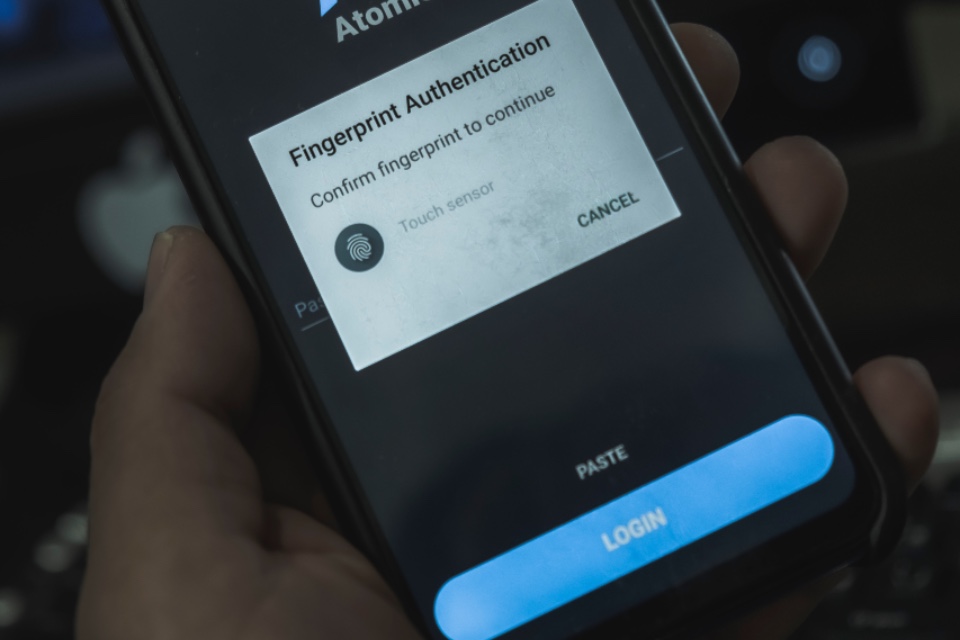
One of the significant shifts in this area is the adoption of biometric technologies. Biometric verification, using unique biological characteristics like fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris scans, offers a higher level of security compared to traditional password-based methods. This technology is particularly effective in mitigating risks such as identity theft, as biometric data is extremely difficult to replicate or steal.
Another critical development is the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to access a service or complete a transaction. This could include something the user knows (like a password), something the user has (like a smartphone), and something the user is (like a fingerprint). MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, making it a valuable tool in the anti-fraud toolkit.
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in digital identity verification is also gaining traction. These technologies can analyse vast amounts of data to detect patterns and anomalies indicative of fraudulent activity. AI-driven systems can also learn and adapt over time, becoming more effective at identifying and preventing fraud.
Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on creating a seamless user experience in identity verification processes. Balancing security with convenience is crucial, as overly complex or time-consuming processes can lead to user frustration and abandonment of services. The challenge for anti-fraud professionals is to implement robust verification measures without compromising on user experience.
Data privacy and compliance with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) are also critical considerations in digital identity verification. Ensuring that personal data is collected, stored, and processed securely and legally is paramount to maintaining user trust and adherence to legal standards.
In conclusion, the evolution of digital identity verification measures in the UK’s commercial and public sectors reflects a response to the growing sophistication of cyber threats and the demands of a digital-first world. By embracing technologies like biometrics, MFA, AI, and ML, and balancing security with user experience, anti-fraud professionals are establishing more secure, efficient, and user-friendly identity verification systems. This approach not only combats fraud but also fosters trust and confidence among users, which is vital in the increasingly digital landscape of services and transactions.
Are you looking for Digital Identity Verification solutions for your organisation? The Fraud Prevention Summit can help!
Photo by Sajad Nori on Unsplash